Magnetic Ball Chains
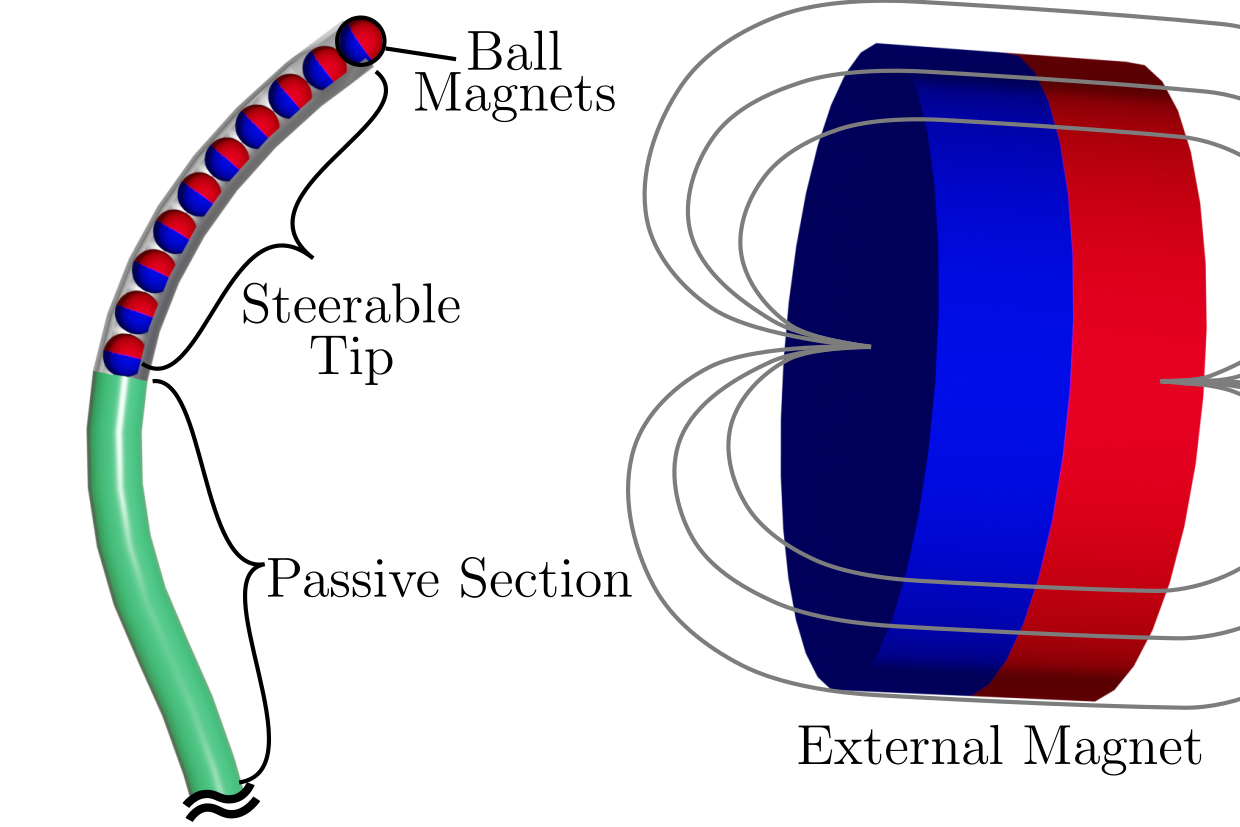
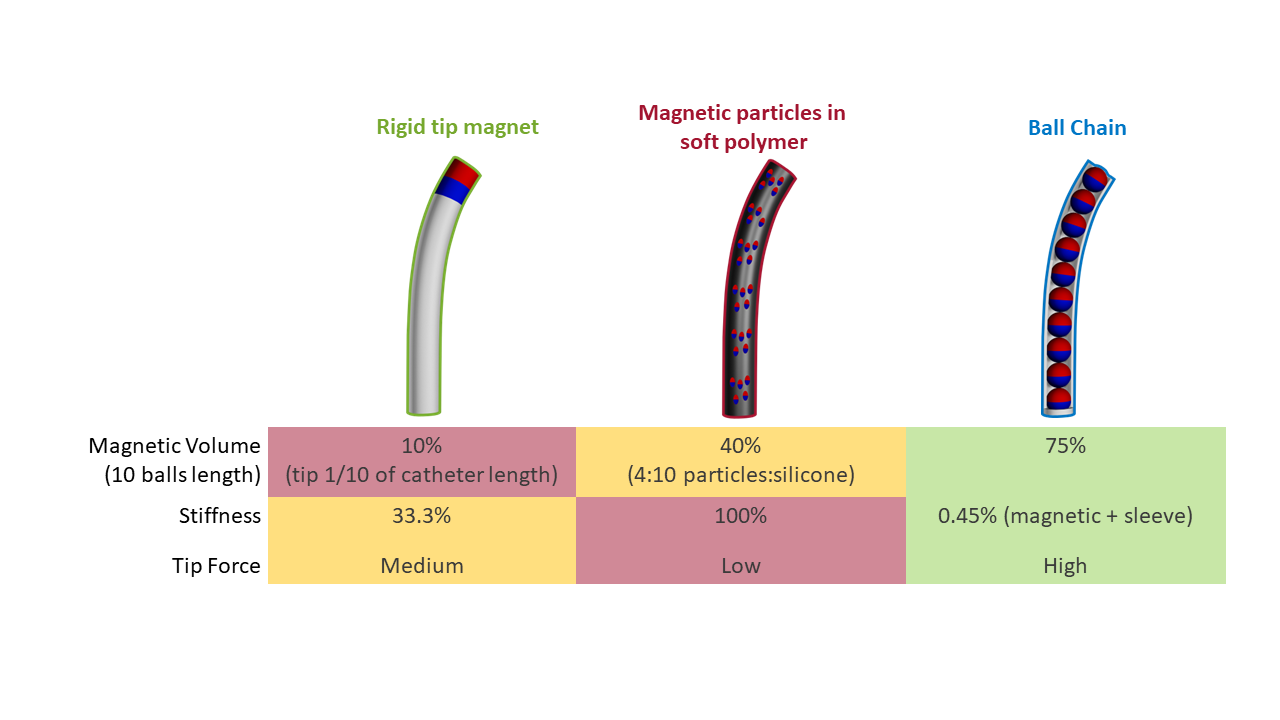
To guarantee high steerability, functional and stable contact forces, I investigated the usage of magnetic ball chains. Millimetre scale spherical magnets naturally bond to each other and align to form a chain. This chain has, generally, a larger magnetic volume (capable of higher forces) and lower stiffness (higher steerability), when compared to embeddeding a magnet at the tip of a flexible tube or using distributed magnetic paticles.
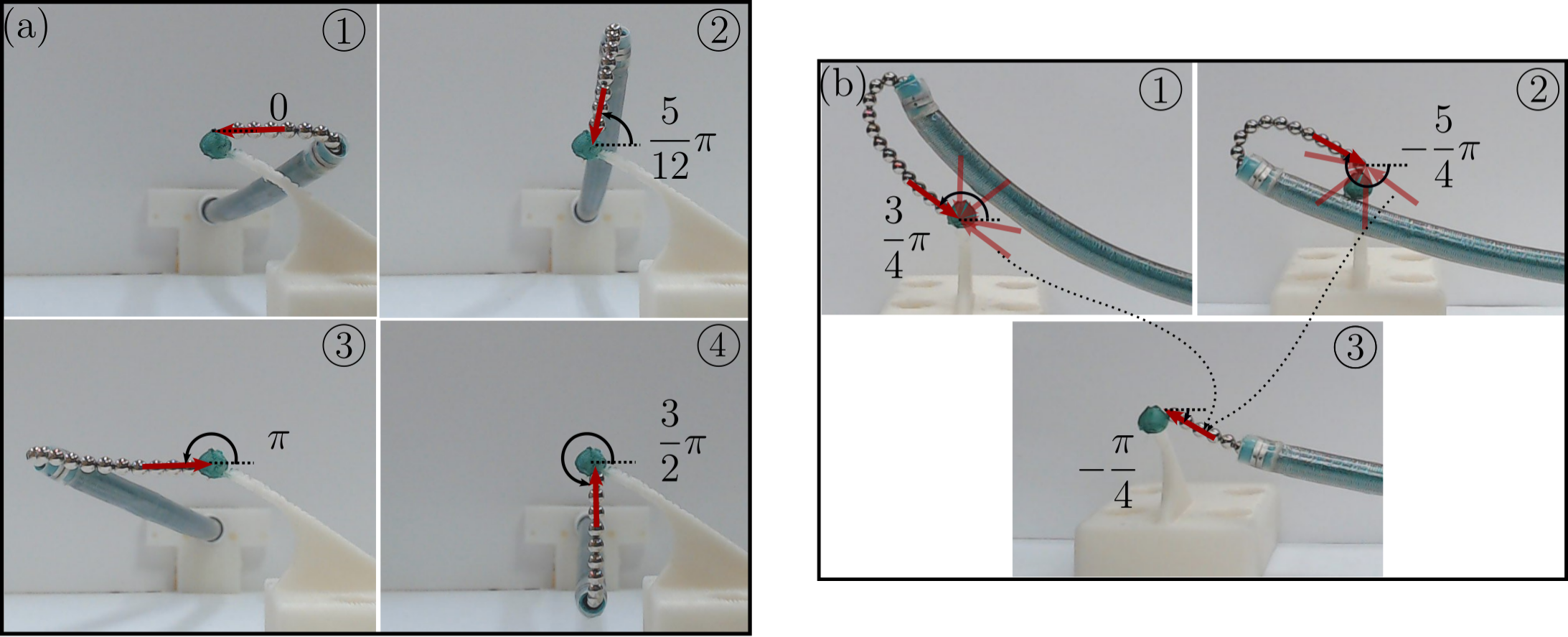
Applying external magnetic field, using a permanent magnet, we can: trace patterns on a surface, guarantee constant contact with moving surface, applying functional forces up to 10g, and ablate tissue. These findings can be mostly useful in treating arrythmia using radiofrequency ablation.
We also investigated how extending the ball chain from a tendon actuated sheath, we can obstain a dexterous workspace. This means that we can approah any point in an area of the workspace with any possible angle of approach. With this approach, we can further control the interaction with the anatomy and guarantee better ablation.
References
2023
-
 Magnetic Ball Chain Robots for Endoluminal InterventionsIn 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2023
Magnetic Ball Chain Robots for Endoluminal InterventionsIn 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2023 - Closed-form Kinematic Model and Workspace Characterization for Magnetic Ball Chain RobotsIn 2023 International Symposium on Medical Robotics (ISMR), 2023